Puzzle 2: Zip
Overview
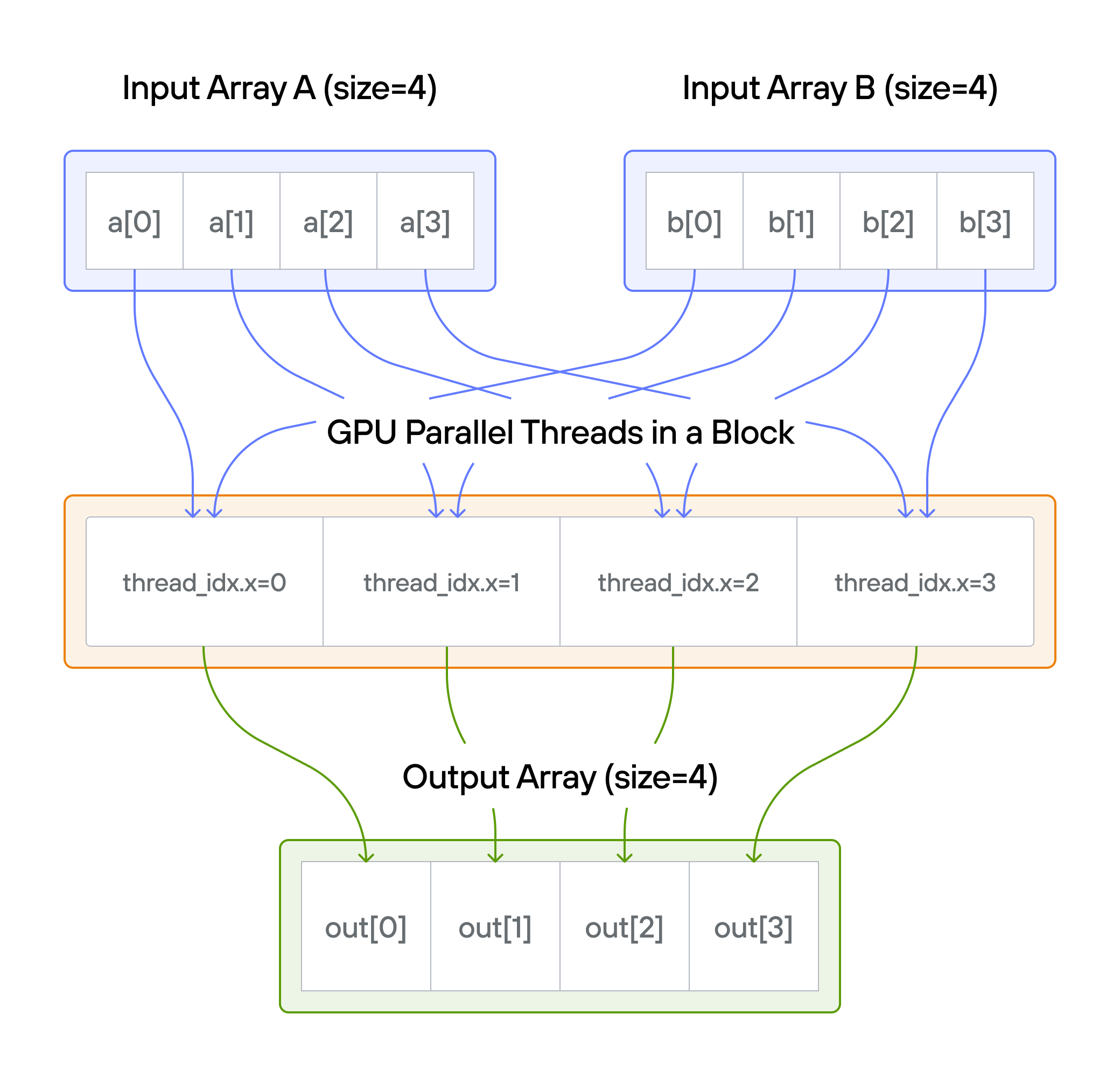
Implement a kernel that adds together each position of vector a and vector b and stores it in output.
Note: You have 1 thread per position.
Key concepts
In this puzzle, you’ll learn about:
- Processing multiple input arrays in parallel
- Element-wise operations with multiple inputs
- Thread-to-data mapping across arrays
- Memory access patterns with multiple arrays
For each thread \(i\): \[\Large output[i] = a[i] + b[i]\]
Memory access pattern
Thread 0: a[0] + b[0] → output[0]
Thread 1: a[1] + b[1] → output[1]
Thread 2: a[2] + b[2] → output[2]
...
💡 Note: Notice how we’re now managing three arrays (a, b, output) in our kernel. As we progress to more complex operations, managing multiple array accesses will become increasingly challenging.
Code to complete
comptime SIZE = 4
comptime BLOCKS_PER_GRID = 1
comptime THREADS_PER_BLOCK = SIZE
comptime dtype = DType.float32
fn add(
output: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
a: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
b: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
):
i = thread_idx.x
# FILL ME IN (roughly 1 line)
View full file: problems/p02/p02.mojo
Tips
- Store
thread_idx.xini - Add
a[i]andb[i] - Store result in
output[i]
Running the code
To test your solution, run the following command in your terminal:
pixi run p02
pixi run -e amd p02
pixi run -e apple p02
uv run poe p02
Your output will look like this if the puzzle isn’t solved yet:
out: HostBuffer([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
expected: HostBuffer([0.0, 2.0, 4.0, 6.0])
Solution
fn add(
output: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
a: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
b: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
):
i = thread_idx.x
output[i] = a[i] + b[i]
This solution:
- Gets thread index with
i = thread_idx.x - Adds values from both arrays:
output[i] = a[i] + b[i]
Looking ahead
While this direct indexing works for simple element-wise operations, consider:
- What if arrays have different layouts?
- What if we need to broadcast one array to another?
- How to ensure coalesced access across multiple arrays?
These questions will be addressed when we introduce LayoutTensor in Puzzle 4.