Puzzle 3: Guards
Overview
Implement a kernel that adds 10 to each position of vector a and stores it in vector output.
Note: You have more threads than positions. This means you need to protect against out-of-bounds memory access.
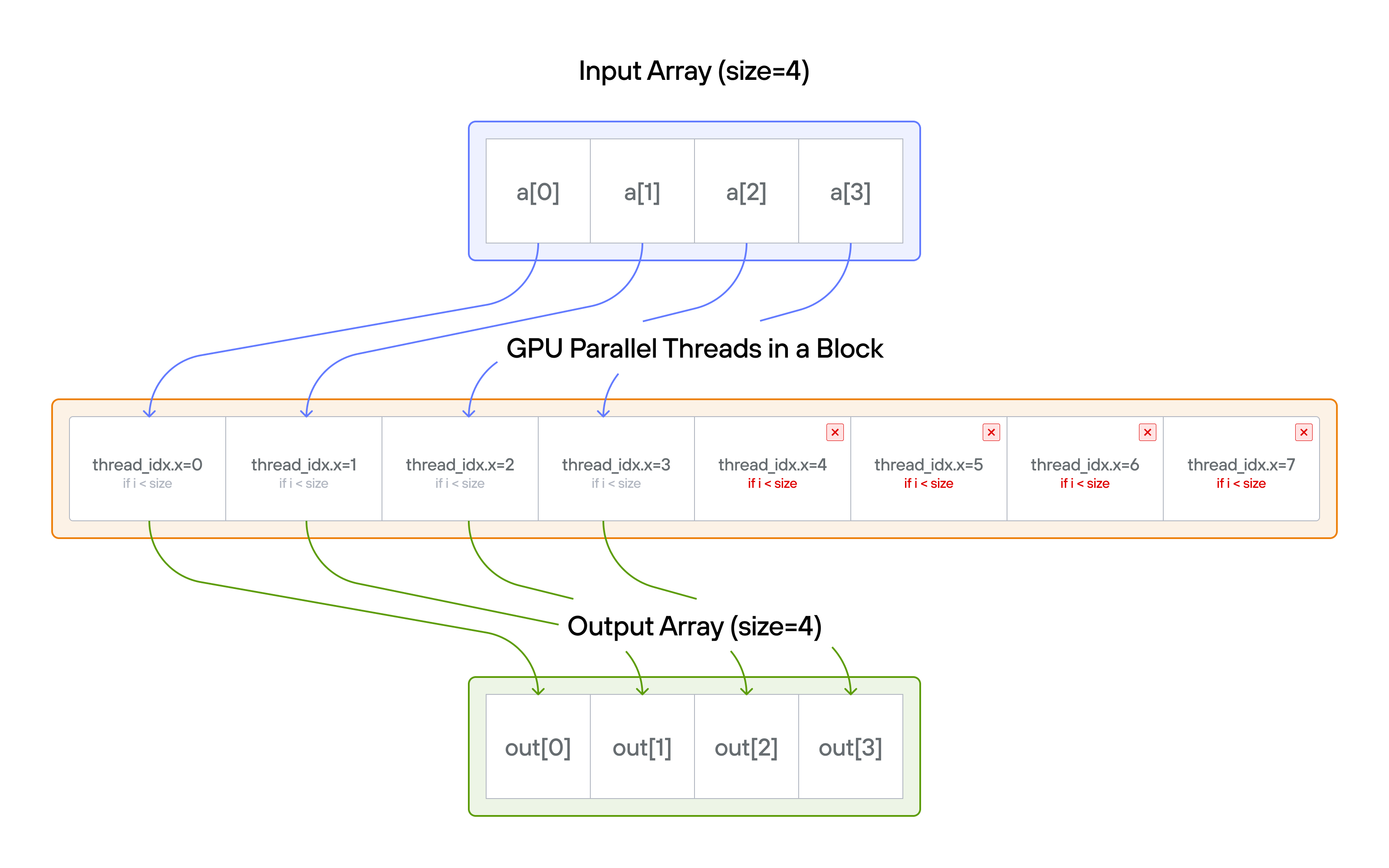
Key concepts
This puzzle covers:
- Handling thread/data size mismatches
- Preventing out-of-bounds memory access
- Using conditional execution in GPU kernels
- Safe memory access patterns
Mathematical description
For each thread \(i\): \[\Large \text{if}\ i < \text{size}: output[i] = a[i] + 10\]
Memory safety pattern
Thread 0 (i=0): if 0 < size: output[0] = a[0] + 10 ✓ Valid
Thread 1 (i=1): if 1 < size: output[1] = a[1] + 10 ✓ Valid
Thread 2 (i=2): if 2 < size: output[2] = a[2] + 10 ✓ Valid
Thread 3 (i=3): if 3 < size: output[3] = a[3] + 10 ✓ Valid
Thread 4 (i=4): if 4 < size: ❌ Skip (out of bounds)
Thread 5 (i=5): if 5 < size: ❌ Skip (out of bounds)
💡 Note: Boundary checking becomes increasingly complex with:
- Multi-dimensional arrays
- Different array shapes
- Complex access patterns
Code to complete
comptime SIZE = 4
comptime BLOCKS_PER_GRID = 1
comptime THREADS_PER_BLOCK = 8
comptime dtype = DType.float32
fn add_10_guard(
output: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
a: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
size: UInt,
):
i = thread_idx.x
# FILL ME IN (roughly 2 lines)
View full file: problems/p03/p03.mojo
Tips
- Store
thread_idx.xini - Add guard:
if i < size - Inside guard:
output[i] = a[i] + 10.0
Running the code
To test your solution, run the following command in your terminal:
pixi run p03
pixi run -e amd p03
pixi run -e apple p03
uv run poe p03
Your output will look like this if the puzzle isn’t solved yet:
out: HostBuffer([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
expected: HostBuffer([10.0, 11.0, 12.0, 13.0])
Solution
fn add_10_guard(
output: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
a: UnsafePointer[Scalar[dtype], MutAnyOrigin],
size: UInt,
):
i = thread_idx.x
if i < size:
output[i] = a[i] + 10.0
This solution:
- Gets thread index with
i = thread_idx.x - Guards against out-of-bounds access with
if i < size - Inside guard: adds 10 to input value
You might wonder why it passes the test even without the bound-check! Always remember that passing the tests doesn’t necessarily mean the code is sound and free of Undefined Behaviors. In puzzle 10 we’ll examine such cases and use some tools to catch such soundness bugs.
Looking ahead
While simple boundary checks work here, consider these challenges:
- What about 2D/3D array boundaries?
- How to handle different shapes efficiently?
- What if we need padding or edge handling?
Example of growing complexity:
# Current: 1D bounds check
if i < size: ...
# Coming soon: 2D bounds check
if i < height and j < width: ...
# Later: 3D with padding
if i < height and j < width and k < depth and
i >= padding and j >= padding: ...
These boundary handling patterns will become more elegant when we learn about LayoutTensor in Puzzle 4, which provides built-in shape management.